A Decision Support System for Ergonomic Construction Design
Construction workers and the decision support system software: (left 2 images) Workers prepares to move a panel in photo and program, and (right 2 images) Workers installing the panel.

Goals & Objectives
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs) remain prevalent among residential construction workers. Premanufacturing (or industrialization) is a contemporary trend in this sector, one important aspect of which is the use of panelized walls that are generated by a designer. While this approach provides increased efficiencies, centralization of design provides an opportunity to promote ergonomics in the design process and is critical given the physical demands involved in building with panels. We are developing decision support system (DSS) for panelized design and construction. The DSS facilitates a more proactive approach to ergonomics in panelized construction, consistent with the philosophy of prevention through design (PtD).
A primary advantage in our approach is the inclusion of both ergonomics and productivity as fundamental components that are both improved. As such, it addresses the need to support the economic and/or business case for PtD, specifically by providing information relevant to necessary financial considerations in decision-making and an understanding of the financial implications of PtD.
Project Approach & Activities
Currently we are working on three specific aims that will be met through three studies, each involving combinations of interviews with target users and workers, software development, and data collection/experiments conducted both in the lab and field. The first aim is to improve and refine the DSS. The second aim is to facilitate DSS implementation (or transfer) by adapting the system to user needs, determining the effects on the panel manufacturer, and completing simulation-based assessments of efficacy (i.e., at reducing exposures to risk factors for WMSDs). The third aim is to demonstrate through a field-based study the actual effectiveness of the DSS in terms of reducing risk factor exposures.
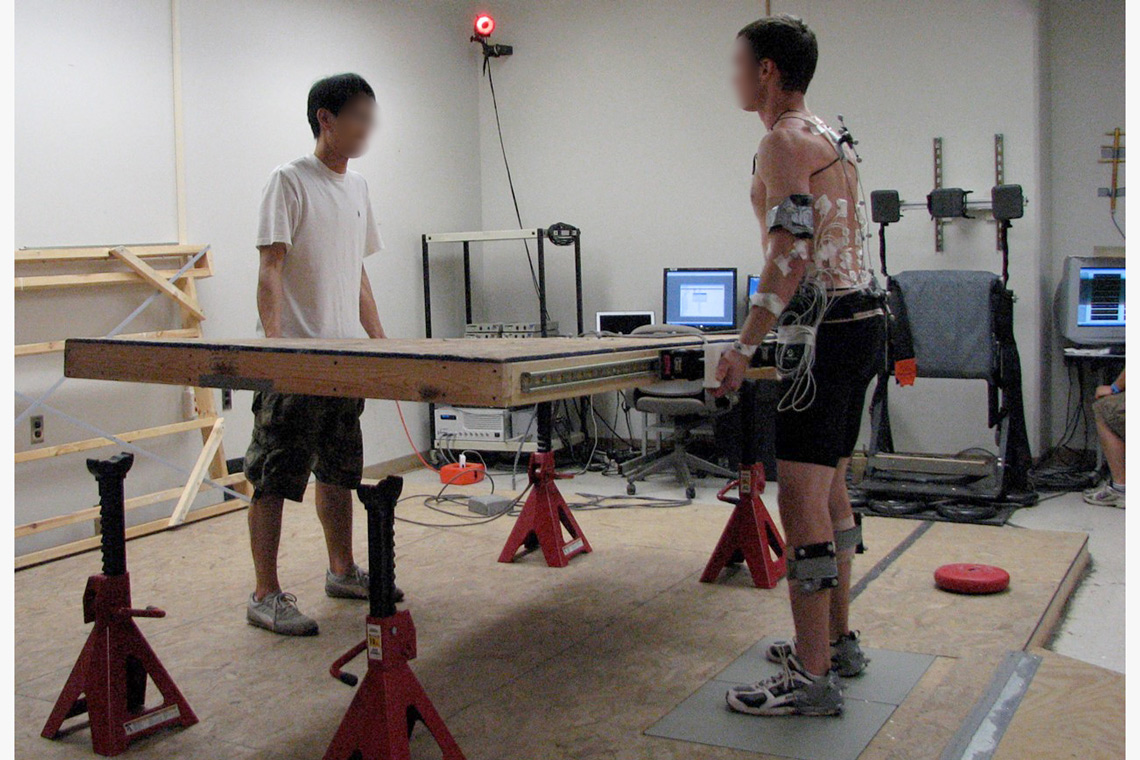
Lab-based task reactions of manual tasks involved in panelized construction
Selected Outputs and Outcomes
- Kim, S., Seol, H., Ikuma, L.H. and Nussbaum, M.A. (2008) Knowledge and opinions of designers of industrialized wall panels regarding incorporating ergonomics in design. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics. 38, 150-157.
- Nussbaum, M.A., Shewchuk, J.P., Kim, S., Seol, H. and Guo, C. (2009) Development of a decision support system for residential construction using panelized walls: approach and preliminary results. Ergonomics. 52, 87-103.
- Kim, S., Nussbaum, M.A. and Jia, B. (2011) Low back injury risks during construction with prefabricated (panelised) walls: effects of task and design factors. Ergonomics. 54, 60-71.
- Jia, B., Kim, S. and Nussbaum, M.A. (2011) An EMG-based model to estimate lumbar muscle forces and spinal loads during complex, high-effort tasks: development and application to residential construction using prefabricated walls. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics. 41, 437-446.
- Kim, S., Nussbaum, M.A. and Jia, B. (2012) The benefits of an additional worker are task-dependent: assessing low-back injury risks during prefabricated (panelized) wall construction. Applied Ergonomics. 43(5): 843-849.
- Shewchuk, J and Guo, C. (2012) Panel stacking, panel sequencing, and stack locating in residential construction: a lean approach. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management. 138(9): 1006-1016.
Decision support software (DSS) is being generated for performing all design and planning activities in panelized residential construction. A prototype of the DSS was completed earlier, and is currently under continuing development and evaluation. This software consists of panelization (breaking walls into panels), stacking (determining how to arrange panels into stacks for delivery), construction sequencing (order in which panels pulled from stacks) and construction planning (what tasks used to erect each panel, how many workers, which particular workers). Also includes a discrete-event panelized residential construction simulator and animator, so that any planned construction process can be simulated and animated (in 3D). Software coded in C++ (Visual Studio 2010), implemented via Web-based user interface (ASP.NET). Simulator developed using object-oriented animation classes developed for this research; animation via PROOF 3D general-purpose animation software.
Faculty and Facility
PI: Maury A. Nussbaum, Ph.D.; Co-Investigators, John P. Shewchuk, Ph.D. and Michael J. Agnew, Ph.D.
Student Researchers
Sunwook Kim, Alireza Sedighi, Sourish Sarkar, Sudarshan Gopinath, Cheng Guo, Courtney Haynes, Bochen Jia.
Funding Source
"Decision support system for ergonomic construction design: Phase II”, NIOSH. (09/01/09-01/31/15) PI: M.A. Nussbaum, Co-Is: J.P. Shewchuk and M.J. Agnew. Subproject within U60 OH009761 (PI: Kleiner).
"Decision support tool for ergonomic construction design”, NIOSH. (09/15/04-09/14/09) PI: M.A. Nussbaum, co-I: J.P. Shewchuk. Subproject within U19 OH008308 (PI: Kleiner).
Sector: Construction
Discipline: Musculoskeletal Disorders
PI: Maury Nussbaum (Virginia Tech)
Co-Is: John Shewchuk (Virginia Tech), Michael Agnew (Virginia Tech)


